Acids and Bases Cheat Sheet
Acids and Bases Cheat Sheet
Matters can be classified in many ways. Acids and bases are another way of classification of matters. Most of the reactions taking place in water solutions are in acid or base mediums. Definitions of acids and bases are given by Arrhenius and Bronsted -Lowery.
1) Definition of Arrhenius :
Arrhenius defines acids as " in water solutions matters that give H+ ion are called acid “. Example of acids is;
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl-
Arrhenius defines bases as " in water solutions matters that give OH- ion are called bases “. Example of bases is;
KOH(s) → K+(aq) + OH-(aq)
2) Definition of Bronsted-Lowry :
They define acids and bases like;
“Acids are matters that donates H+ and bases are matters that accept H+ ion.”
HCl(g) + NH3 (g) → NH4+(s) + Cl-(s)
In this reaction, HCl donates H+ ion so it is acid and NH3 accepts H+ ion, it is base.
CO3 -2+ H2O → HCO3 - + OH-
Some Properties of Acids:
- Their taste is sour like, lemon, orange.
- Their solubility in water is high.
- Their water solutions conduct electric current.
- Compounds including CO3-2 and HCO3 - produce CO2 gas;
Some Properties of Bases:
- Their taste is bitter like shampoo.
- Their solutions with water conduct electric current.
- When we touch basic matter, we feel them slippery.
- Their solubility in water is low with respect to acids.
- Bases turn red litmus to blue.
- They do not react with metals. However, some of the metals like Zn and Al react with bases and form H2 gas and salt. These metals are called amphoteric metals. They behave like acid for base and base for acid.
Oxides
Compounds of any element with water are called oxides . We examine them under four titles; acidic and basic oxides, neutral oxides, amphoteric oxides and peroxides;
1) Acidic Oxides: They are oxides which combine with bases and form salt. SO2, SO3 , CO2, N2O5 are example of acid oxides.
2) Basic Oxides: They combine with acids and form salt. Metal oxides show this property like; Na2O, CaO.
3) Neutral Oxides: They are do not react with acids and bases. Neutral oxides do not react with water and form acid or base. NO, N2O and CO are some examples of neutral oxides.
4) Amphoteric Oxides: These oxides react with acids and bases and form salt. ZnO and Al2O3 are examples of amphoteric oxides. Example of these reactions is given below;
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O
5) Peroxides: Compounds including (O2)-2 in their structure are called peroxides. Example of peroxides is given below;
H2O2: Hydrogen Peroxide
Strong Acids and Weak Acids:
Strength of acid is related to ionization of acids in water. Some of the acids can ionize 100 % in water solutions, we call them “strong acid s”. HCl, HNO3, HBr, HI, H2SO4 are examples of strong acids.On the contrary, some of the acids can not ionize like strong acids. We call acids partially ionize in solutions “weak acid “. CH3COOH, HF, H2CO3 are examples of weak acids.
Strong and Weak Bases:
Bases ionize completely in solutions are called “strong bases” . NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2 and bases including OH- ion are strong bases. Bases that ionize partially in solutions are called “weak bases “. NH3 is an example of weak base.
Water ionize as given below;
H2O(l) ↔ H+(aq) + OH-(aq)
In pure water concentrations of H+ and OH- ions are equal to each other and at 25 0C, they have concentration 1x10-7 M. Since concentration of ion in pure water is too low, it is a bad electric conductor.
If acid is added to pure water;
[H+]>1x10-7 M and [OH-]<1x10-7
If base is added to pure water;
[OH-]>1x10-7 M and [H+]<1x10-7
In liquid solutions, to state concentrations of H+ and OH- ions pH and pOH concepts are used. We can show pH and pOH in terms of concentration as;
pH=-log[H+]
and
pOH=-log[OH-]
Solution having molar concentration of H+=10-2 M has pH=2 and solution having molar concentration of OH-=10-5 has pOH=5.
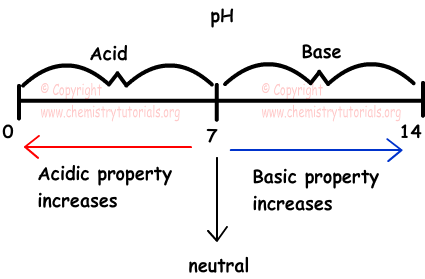
- If 7>pH>0 acidic solution
- If 14>pH>7 basic solution
- If pH=7 neutral solution