Polarity of Bonds
Polarity of Bonds
In bonds, forming between two same atom, electrons are attracted by equal forces. We call these bonds nonpolar covalent bonds . H2, O2 and N2 has nonpolar covalent bond. If covalent bond is formed between two different atoms having different electronegativity, then force acting on shared electron by the atoms becomes different. These types of bonds are called polar covalent bonds . HCl, HF, CO are examples of polar covalent bond. Molecules having polar bonds can be polar or nonpolar. To have an idea about whether molecule is polar or nonpolar you should look at molecule geometry.
Hybridization and Bonding Geometry
We have learned that atoms can form bonds equal to number of half filled orbitals. On the contrary, when we look at molecule geometry or unexpected number of bonds of II A, III A and IV A groups, we explain it with another concept that is called hybridization . Now we examine each group elements and their bonding capacities with the help of this concept.
I A Group Bonds:
Li element is an example of I A group, let me examine bond between Li and H atoms.
Electron configuration of Li is;
Li: 1s22s1
As you can see Li has one half filled orbital and can form one bond. Thus Li and H share one electron and form following bond;
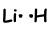
This molecule is linear and polar .As you can guess all diatom molecules are linear.
II A Group Bonds: (sp hybridization)
Be element in this group forms bonds with H and F; BeH2 and BeF2. Electron configuration of Be is;
Be: 1s22s2
As it seen from electron configuration, Be do not have half filled orbitals. We expect that it can not form bond. On the contrary experiments done on this show that hybridization make Be form bonds.
While forming bond, one electron in 2s orbital transferred to the 2p orbitals and Be has two half filled orbitals and have capacity to form 2 bonds. Since the electrons are in different orbitals (2s and 2p) we expect that their properties are different. On the contrary, experiments show that these bonds have same characteristics, they are same. This is also explained with hybridization.
These orbitals repel each other and placed with an 180 0 angle to each other and form following bonds;
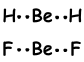
This molecule is linear and nonpolar . Bonds are polar but equivalent force acting on Be with 180 0 angle is zero, so molecule is nonpolar.
III A Group Bonds: (sp2 hybridization)
5B element in this group forms bonds with H and F; BeH3 and BeF3. Electron configuration of B is;
B: 1s22s22p1
As it seen from electron configuration, B has one half filled orbital and can form one bond. But wee see that it forms 3 bonds. This is an example of sp2 hybridization. One electron of 2s orbital is transferred to 2p orbital and it has now 3 half filled orbitals and can form 3 bond. These three bonds are same again as in the case of sp hybridization and by repelling each other they are located with and 120 0angle. We show these electrons and bond with Lewis dot formula ;
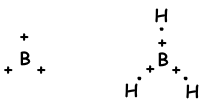
Molecule has trigonal planar geometry. This molecule is also nonpolar despite of all bonds are polar. Since electrons are placed with an 120 0 angle, equivalent force of them is zero, so molecule is nonpolar .
IV A Group Bonds: (sp3 hybridization)
6C element in this group forms bonds with H and F; CH4 and CF4. Electron configuration of C is;
C: 1s22s22p2
As it seen from electron configuration, C has two half filled orbitals and can form two bonds. But wee see that it forms 4 bonds. This is an example of sp3 hybridization. One electron of 2s orbital is transferred to 2p orbital and it has now 4 half filled orbitals and can form 4 bonds now. These four bonds are same again as in the case of sp and sp2 hybridization and by repelling each other they are located with and 1090 angle. We show these electrons and bond with Lewis dot formula ;
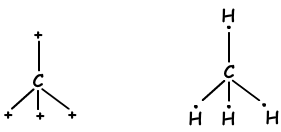
These molecules have shape tetrahedral and they are nonpolar molecules .
V A Group Bonds: (sp3 hybridization)
7N element in this group forms bonds with H; NH3. Electron configuration of N is;
N: 1s22s22p3
By looking at orbital structure of this element, we say that it can form 3 bonds and there is no need hybridization. On the contrary, experiments done on this element show that, hybridization must occur to have 1070 angle between bonds. Thus, one 2s and three 2p orbitals are mixed and four sp3 hybrid orbital. One of these orbitals have 2 electrons and do not join bonding, but it changes angle in the case of tetrahedral 109 0 to 107 0 and form new shape “trigonal pyramidal “. Since charges are not distributed equally this molecule is polar . Shape of NH3bonds;
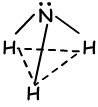
VI A Group Bonds: (sp3 hybridization)
8O element in this group forms bonds with H and F; H2O and OF2. Electron configuration of O is;
O: 1s22s22p4
Oxygen can form two bonds but experiments show that angle between bonds is 104,50, this can only be possible with hybridization. One s and 3 p orbitals are mixed and 4 sp hybrid orbitals are formed. These four orbitals contain 6 electrons and 2 of the orbitals are half filled and they form 2 bonds. Shape of molecule becomes bent and molecule is polar .
Example: In which one of the following compounds, both molecule and bonds are polar.
(4Be, 5B, 6C, 8O, 16S, 17Cl)
I. BeCl2
II. CO2
III. SCl2
IV. BCl3
V. CCl4
Solution:
I. Lewis dot formula of BeCl2 is given below ;

Shape of molecule is linear, and it is nonpolar.
II. Lewis dot formula of CO2 is given below ;
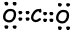
Shape of molecule is linear, and it is nonpolar.
III. Lewis dot formula of SCl2 is given below ;
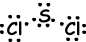
Resultant bond vector is not zero, thus molecule is polar and bonds are also polar.
IV. Lewis dot formula of BCl3is given below ;
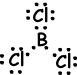
Shape of molecule is trigonal planar. Since resultant bond vector is zero molecule is nonpolar.
V. Lewis dot formula of CCl4 is given below ;
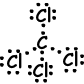
Shape of molecule is tetrahedral, and molecule is nonpolar.
Thus, both bonds and structure of molecule of SCl2 are polar.