Gases Exam 3 and Problem Solutions
Gases Exam 3 and Problem Solutions
1. Find volume of 0,5mol CH4under 3,28 atm pressure and 400 0K temperature.
Solution:
P=3,28 atm, n=0,5mol, T=400 0K, R=0,082, V=?
We use ideal gas law;
P.V=n.R.T
3,28.V=0,5.0,082.400
V=5 liters
2. If 6,4 g CH4 has pressure 0,5 atm and volume 2 liters, find pressure of 9 g C2H6 having 1 liter volume under constant temperature.(C=12, H=1)
Solution:
We first find mole of given matters;
nCH4=6,4/16=0,4mol
nC2H6=9/30=0,3mol
Since temperature is constant we write ideal gas law as given below;
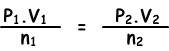
(0,5.2)/0,4=(P2.1)/0,3
P2=0,75 atm
or P2= 57 cm Hg
3 . Find density of O2 under 27 0C temperature and 1,23 atm pressure. (O=16)
Solution:
T=27 + 273=300 0K
If we write ideal gas law for density, we get following equation;
d=(P.M)/(R.T)
where M is molar mass of O2.
d=(1,23.32)/(0,082.300)
d=1,6g/liter
4. If we open the taps given in the picture below, find final temperature of gases.

Solution:
We use following equation to find final pressure of gas mixture;
P1.V1 + P2.V2 + P3.V3 = Pfinal.Vfinal
3.2 + 4.3 + 0.5 =Pfinal.(2+3+5)
6 + 12=Pfinall.10
Pfinal=1,8 atm
5. When we open the taps given in the picture below, find changes in the pressures of gases.

Solution:
We should find final pressure of system to make comparison.
P1.V1 + P2.V2 + P3.V3 = Pfinal.Vfinal
P.V + 2P.2V + 3P.V = Pfinal.(V+2V+V)
Pfinal=2P
Thus,
I. Pressure of first container increase
II. Pressure of second container stays constant
III. Pressure of third container decreases